As more and more Electric Vehicle (EV) models are getting launched in Two Wheeler and Four Wheeler, the question of EV Charging in Apartment / building complexes is started to come up. In this article we are trying to answer some basic questions quoting EV charging regulation / policies from the Central Government and Gujarat Government.
- Can a member setup a charging point in the building ?
- What will be the tariff applicable for such charging ?
- Can Housing Society set up Public Charging Stations for its members ?
Definitions
Central Electricity Authority (Measures relating to Safety and Electric Supply) (Amendment) Regulations, 2019 defines Electric vehicle
“Electric Vehicle” means any vehicle propelled, partly or wholly, by an electric motor drawing current from a rechargeable storage battery, or from other portable energy storage devices (rechargeable, using energy from a source off the vehicle at a residential or public electricity service);
Central Electricity Authority (Technical Standards for Connectivity of the Distributed Generation Resources) Amendment Regulations, 2019 define Charging Point
“Charging Point” means a facility for recharging of batteries of electric vehicle for private or public non-commercial use, connected at 415/220 Volts.
Ministry of Power: Charging Infrastructure for Electric Vehicle (EV) – Revised Guidelines & Standards
Public Charging Station (PCS) shall mean an EV charging station where any electric vehicle can get its battery recharged.
Ministry of Power: Charging Infrastructure for Electric Vehicle (EV) – Revised Guidelines & Standards
The Ministry of Power (MoP) issued the Charging Infrastructure Guidelines and Standards for public charging infrastructure, which laid out an enabling framework for implementation. In its capacity as a legislative authority, the MoP clarified that the operation of EV charging services did not require licensing under the Electricity Act 2003.
Also below are keys points in guidelines related to housing societies and building complex:
- Owners may charge their electric vehicle at their residence / offices using their existing electricity connections.
- The minimum infrastructure requirement do not apply to Private Charging Points meant for self-use of individual EV owners (non-commercial basis)
- Public Charging Station may also be installed by Housing Societies, Malls, Office Complex, Restaurants, Hotels etc. with a provision to allow charging of Visitor’s vehicle which are permitted to come in its premises.
- The Tariff applicable for domestic consumption of electricity shall be applicable for domestic charging.
Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs : Model Building Byelaws 2016 – Amendment
The Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs (MoHUA) amended the Model Building Byelaws 2016 and the Urban and Regional Development Plans Formulation and Implementation Guidelines 2014 (URDPFI) to include provisions for EV charging in building. These are recommended amendments for states to implement.
Amendments are made to Chapter 10 (Sustainability and Green Provisions) of the MBBL-2016, with Section 10.4 titled “Electric Vehicle Charging Infrastructure”.
- Charging infrastructure shall be provided for EVs at 20% of all ‘vehicle holding capacity’/’parking capacity’ at the premises.
- The building premises will have to have an additional power load, equivalent to the power required for all charging points to be operated simultaneously, with a safety factor of 1.25.
The amendments are applicable to all buildings except independent residences. Further provision norms for slow chargers (SC) are provided based on the number of EVs to be serviced, by segment. Norms for fast chargers (FCs) are not compulsory
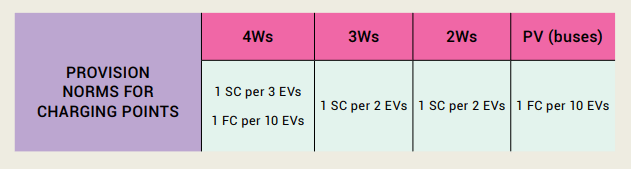
While building byelaws are applicable only to new buildings, existing buildings should also integrate EV charging as an amenity for occupants and visitors. The number of chargers to be installed can be estimated based on EV charging demand and available power capacity of the electricity connection. In some cases, governments may issue orders to commercial and institutional establishments to install EV charging infrastructure.
Niti Aayog: Handbook of Electric Vehicle Charging Infrastructure Implementation
Private Charging
Usage: Dedicated charging for personal EV or EV fleet owned by one entity
Locations: Independent homes, dedicated parking spots in apartments / offices; for fleets – any location with land availability
Ownership: Individual EV owners, EV fleet owners / operators
Operation: Self-operated or CPO-managed (for EV fleet charging)
Semi-Public Charging
Usage: Shared charging for a restricted set of EV users
Locations: Apartment complexes, office campuses, gated communities, shopping malls, hospitals, universities, government buildings, etc.
Ownership: Host properties, Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) & Charge Point Operators (CPOs)
Operation: CPO-managed
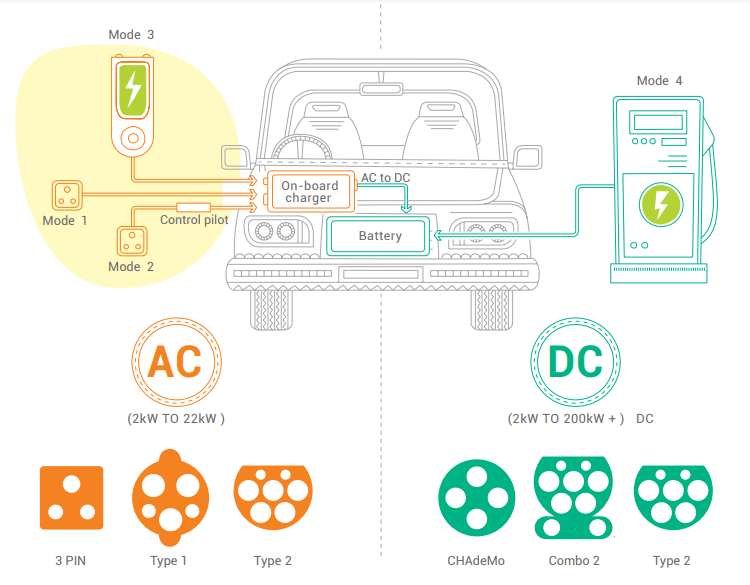
Type of Charging Port
Public Charging Infrastructure (PCI) – Requirement (Power Ministry)
If Buildings are putting up Charging for its members / visitors, it will fall under the definition of Public Charging Station. Below infrastructure requirement will have to be fulfilled
- Every Public Charging Station (PCS) will comply with following
- An exclusive transformer with all related substation equipment including safety appliance, if required by supply code as approved by Appropriate Electric Regulatory Commission
- Appropriate Civil Works
- Appropriate Cabling and Electrical work ensuring safety
- Adequate space for charging and entry / exit of vehicles
- Appropriate fire protection equipment and facilities
- Public charging station will have one or more chargers or any combination of chargers in one or more electric kiosk / board
- Charging station for (Two / Three Wheelers) e-vehicles shall be free to install any chargers other than those specified above subject to compliance of technical and safety standards as laid down by CEA
- Tie up with at least one online Network Service Provider (NSPs) to enable advance remote / online booking of charging slots by EV owners. Such online information to EV owners should also including information regarding location, type and number of chargers installed / available, service charges for EV Charging etc.
- Share charging station data with the appropriate State Nodal Agency (SNA) and adhere to protocols as prescribed by Central Nodal Agency (CNA) ie., Bureau of Energy Efficiency for this purpose. The CNA and SNA shall have access to this database.
- Public charging station for EVs shall comply with the provision of Central Electricity Authority (Technical Standards for Connectivity of the Distributed Generation Resources) Amendment Regulations, 2019 and Central Electricity Authority (Measures relating to Safety and Electric Supply) (Amendment) Regulations, 2019
- Electric Vehicle Supply Equipment (EVSE) should have been type tested by an agency / lab accredited by National Accreditation Board for Testing and Calibration Laboratories (NABL) from time to time
- The above minimum infrastructure requirements do not apply to Private Charging Points meant for self-use of individual EV Owners (non-commercial basis)
- Captive charging infrastructure for 100% internal use for a company’s own / leased fleet for its own use will not be required to install chargers as per 3.1 and to have National Service Providers (NSP) tie up.
- Public Charging Station may also be installed by Housing Societies, Malls, Office Complex, Restaurants, Hotels etc. with a provision to allow charging of Visitor’s vehicle which are permitted to come in its premises.
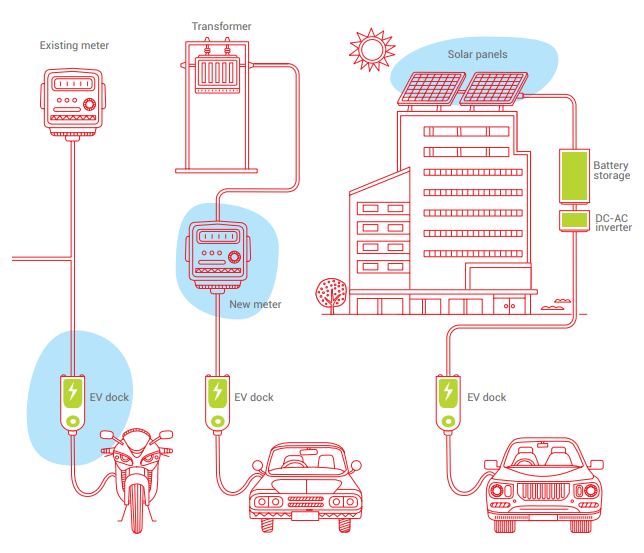
Tariff for Supply of Electricity to EV Public Charging Station
- The tariff for supply of electricity to Public EV Charging Station shall be a single part tariff and shall not exceed the “Average Cost of Supply” till 31’st March, 2025. The same tariff shall be applicable for Battery Charging Station (BCS)
- The tariff applicable for domestic consumption shall be applicable for domestic charging.
- The separate metering arrangement shall be made for PCS so that consumption may be recorded and billed as per applicable tariff for EV charging stations.
- DISCOMs may leverage on funding from the Revamped Distribution Sector Scheme (RDSS) under “Part A – Distribution Infrastructure” for the general upstream network augmentation necessitated due the upcoming charging infrastructure in various areas. The cost of such work carried out by the DISCOMs with the financial assistance from the Government of India under the Revamped Scheme shall not be charged from the customer for Public Charging Stations for EVs.
Service Charges of PCB
The State Nodal Agency shall fix the ceiling of the Service Charges to be charged by the public charging stations.
Gujarat State Electric Vehicle Policy – 2021
- All housing and commercial establishments shall give a ‘No Objection Certificate’ (NOC) to its members who wish to install charging stations with designated parking spaces.
- The State Distribution Licensees (DisComs) shall allow charging of EVs from the existing connection of a Consumer at the existing tariff, except from agriculture connection.
Gujarat Electricity Regulatory Commission : Tariff Orders for the Electric Utilities: 2018
The Commission is aware about the initiative taken by the Government to encourage use of electric vehicles. One of the challenges in this regard is identified as lack of EV charging infrastructure. Commission would like to clarify that the consumers getting electricity supply under regular tariff categories may use electricity supply for EV charging under same consumer category.
Further, in order to promote creation of new EV charging facilities, Commission decided to introduce special tariff category for exclusive EV Charging infrastructure with Fixed Charges of Rs. 25 per month per installation and Energy Charges of Rs. 4.10 per kWh for LT consumers and Demand Charges of Rs. 25 per kVA per month and Energy Charges of Rs. 4.00 per kWh for HT Consumers. Such consumers are also required to pay the FPPPA charges as applicable from time to time.
UGVCL Tariff Schedule Effective: 01-Apr-2020
RATE: LT ELECTRIC VEHICLE (EV) CHARGING STATIONS
This tariff is applicable to consumers who use electricity exclusively for Electric Vehicle
Charging installations.
Other consumers can use their regular electricity supply for charging electric vehicle under same regular category i.e. RGP, RGP (RURAL), GLP, LTMD, NON-RGP NIGHT, LTMDNIGHT, etc. as the case may be.
Building Charing Roadmap
- Phase 1 – Low Adoption
- Install 3 – 5 level 1 charging stations in the common parking.
- Allow members to install charging points in their own parking.
- Phase 2:
- Install smart AC level 1 charge point devices with metering and load balancing capabilities.
- For larger societies with high EV adoption, DC Rapid Charging stations can be installed.
Safety Measures – Building
- Define cabling standards for residents to follow during private installation
- All EV charging points should have a socket-outlet of supply, at least 2.6 feet above the finished ground level.
- Route the cabling through your electrical contractor or have the implementation monitored by your electrical supervisor to avoid any potential threat
- Install a low cost charge point with adequate safety layers to protect against load surges and voltage fluctuations. Charge points with auto-power cutoff option on full charge and additional safety features are safer than a regular 16A socket.
- The EV users should ensure that the compatible adapters and connectors are used for the EV models that would avail the EV charging service.
- A cord extension set or a second supply lead should not be used in addition to the connector used by the EV to connect to the EVSE. The EV parking place shall be such that the connection on the EV when parked for charging shall be within five meters from the EV charging point.
- Fire detection, alarm and control systems should be provided as per relevant Indian Standards.
- The Buildings / Societies should ensure that there are boards / notices clearly displayed at each charge point which would mention the specifications of those charge points.
- The location should preferably be close to the main electrical panel, this will reduce the wiring / cabling costs.
- The parking should either be covered or preferably not be exposed to direct heat. Excessive heat is not good for charging infrastructure and the vehicle’s battery.
- EV charging space should be easily accessible to residents and visitors.
- Building / Society may also approve personal EV chargers if the electricity consumption (including EV charger) remains under the sanctioned load of the house
- EV charging area should preferably be away from the Children’s play areas.
Summary
- Can a member setup a charging point in building ? : Yes after taking No objection certificate (NOC) from the building.
- What will be the tariff applicable for such charging ? : Existing Tariff for Residential Units / Apartment.
- Can Housing Society set up Public Charging Stations for its members ? : Yes, after putting up required infrastructure.
References
- Gujarat State Electric Vehicle Policy‐2021
- Ministry of Power: Charging Infrastructure for Electric Vehicle (EV) – Revised Guidelines & Standards: Jan 2022
- Niti Aayog: Handbook of Electric Vehicle Charging Infrastructure Implementation
- Model Building Bye-laws, 2016
- Amendment in Model Building Bye-Laws (MBBL-2016) for Electric Vehicle Charging Infrastructure.: 2019
- Central Electricity Authority (Technical Standards for Connectivity of the Distributed Generation Resources) Amendment Regulations, 2019
- Central Electricity Authority (Measures relating to Safety and Electric Supply) (Amendment) Regulations, 2019
- EV Charging Guide : RWAs
- Ministry of Power 23/08/2018 R&R dated 13-04-2018
- UGVCL Tariff Schedule Effective: 01-Apr-2020
- Residential EV Charging Guidebook: New Delhi
- Gujarat Electricity Regulatory Commission: Tariff Orders for the Electric Utilities
- India’s Electric Vehicle Sales Trend for 2021
- How to charge your electric vehicle at your apartment
- Tata Power: EV Charing Solutions
- Bolt Earth: Smart EV Charging Stations And Software
- Tariff Schedule 2021-22 for Ahmedabad – Gandhinagar : Torrent Power Ltd

Our appartment in surat , complex of 5 buildings of 11 floors , how to provide a electricity point for each flat holder in parking
to facilitate for EV
Providing a charging point to all flats is not the solution. There are many vendor who have come up (like Ola, Mygate) which are giving charging point in common area and amount is charged to member as per usage
My apartment association has identified areas for common charging station but have not installed it yet. The owners are requesting from 4-5 months, they are not giving noc for private installation and not providing public station as well.
The planned station can serve only 3 cars at a time. What can be done?
There is no clear process defined in electric charging regulation. As per cooperative society act, you can ask a committee to call for a Special General meeting with an agenda for electric charging but it should be signed by the minimum number mentioned as per byelaws. Once such a request is given, the Chairman will have to call a meeting within 1 month of the receipt of request.
Hello,
How can i get the separate meter from GEB DGVCL for Electric Charging Private Station at my home??.
Also is there any green meter for private station home from GEB DGVCL ?